There has been a lot of transformation in the finance world with the advent of decentralized finance, also known as DeFi. The early stages are known as DeFi 1.0. Maker DAO is a very early project that used blockchain and cryptocurrency concepts to perform peer-to-peer lending and borrowing. But with time, it evolved and has finally become DeFi 2.0.
The comprehensive guide given here delves into the realm of DeFi 2.0, which helps explore the newly found features and capabilities that promise to revolutionize the financial sector and extend its influence to other industries. Because of the future of DeFi 2.0, dApp Development is quite popular.
This article will teach us about the innovative solutions and projects that help drive this exciting evolution.
What is DeFi 1.0?
DeFi 1.0 is known as Decentralized Finance 1.0. It is the initial phase of the decentralized application and protocol built based on blockchain networks, mostly Ethereum. During this early phase, DeFi projects focused on creating alternatives to traditional financial services like cryptocurrency exchanges, lending platforms, and stablecoin issuance. While this laid the foundation of decentralized finance, DeFi 1.0 had limitations such as scalability, centralization, and security issues in smart contracts. Such challenges paved the way for the evolution into decentralized finance 2.0, which seeks to address such issues and expand decentralized financial services’ overall capabilities.
What are the Limitations of DeFi 1.0?
DeFi 1.0 is the initial phase of decentralized finance. This has brought groundbreaking innovations to the world of blockchain and finance. However, there were several limitations as well. This prompted the evolution of DeFi 2.0.
Let us take a look at some key limitations of DeFi 1.0:
- Irrespective of the decentralization philosophy of blockchain, DeFi 1.0 protocols have certain points of control. Some individuals influence decision-making. For example, Maker DAO had a small group with some voting power that raised concerns about transparency, censorship resistance, and trust.
- DeFi 1.0 relied a lot on the Ethereum blockchain. This faced scalability issues during times of high demand. Any high gas fees, as well as network congestion, can make handling a large volume of transactions challenging as well as limit the growth of the platform as well as the user base.
- DeFi 1.0 projects were built on smart contracts, which were subject to vulnerabilities. Hackers made the most of such vulnerabilities to steal certain amounts of cryptocurrencies, highlighting the need for better security measures.
- Liquidity in DeFi 1.0 was broken down across different protocols. This leads to lower liquidity levels in individual protocols. The complexity made it easy for users to trade across various platforms while reducing capital efficiency.
- It was essential for users to manage their private keys. These are complex strings of characters. If anyone loses this key, it would mean losing access to their assets, which would create a barrier for those unaware of the technical aspects involved in crypto.
- The DeFi 1.0 platform needs user-friendly interfaces that limit participation to a technically proficient audience. The absence of intuitive interfaces can stop mainstream adoption.
- DeFi 1.0 relied a lot on Ethereum, which resulted in congestion and high gas fees. This kind of dependency also limited the diversity of blockchain options for users.
- DeFi 1.0 lending needs collateral the same as or even more than the loan amount, and that too excluding the potential borrowers.
Such limitations served as a catalyst and led to the evolution of DeFi 2.0. This is the second phase, which aims to overcome challenges and create a secure, scalable, and user-friendly financial ecosystem.
What is DeFi 2.0?
DeFi 2.0 is the after-evolution phase of decentralized finance. This was built on the initial developments. The main focus is improving scalability, security, and user experience while emphasizing decentralization. DeFi 2.0 includes innovations like DAOs, protocol-controlled liquidity, loss insurance, self-repaying loans, and advanced yield farming techniques. Such advancements aim to make DeFi much more accessible, secure, and revolutionary in the financial system. This provides broader global access to financial services. Though there are significant promises involved, at the same time, there are risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and even regulatory challenges necessitating careful consideration by investors as well as participants.
Examples of DeFi 2.0 Projects
DeFi 2.0 has seen the emergence of various innovative projects by pushing the boundaries of what decentralized finance can get.
- Olympus DAO is a pioneer in the field of DeFi 2.0. It focuses on the creation of stable as well as sustainable currency, known as OHM. It uses a unique mechanism where users can lock up OHM tokens in exchange for rewards daily. It helps promote stability as well as liquidity of the ecosystem.
- The Graph, or GRT, is a decentralized indexing protocol that allows developers to access data from different blockchain networks. It plays a major role in providing data infrastructure for DeFi applications. This improves the efficiency as well as functionality.
- Synapse is a decentralized identity and access management platform. It allows users to securely manage their identities and then control access to the data while addressing privacy and other security concerns in DeFi.
- Rarible (RAR) is a decentralized marketplace for non-fungible tokens that helps empower creators to mint, trade, and sell unique digital assets. This plays a major role in the NFT boom and presents new solutions for artists and collectors.
- Convex finance improves yield farming for curve finance liquidity providers. This ensures they receive maximum returns. It improves the trend of projects, improving yielded opportunities within DeFi.
Emerging Trends in DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 is an evolution of decentralized finance that builds upon the foundations of DeFi 1.0, aiming to address its limitations and introduce more robust solutions. Here are some of the emerging trends in DeFi 2.0:
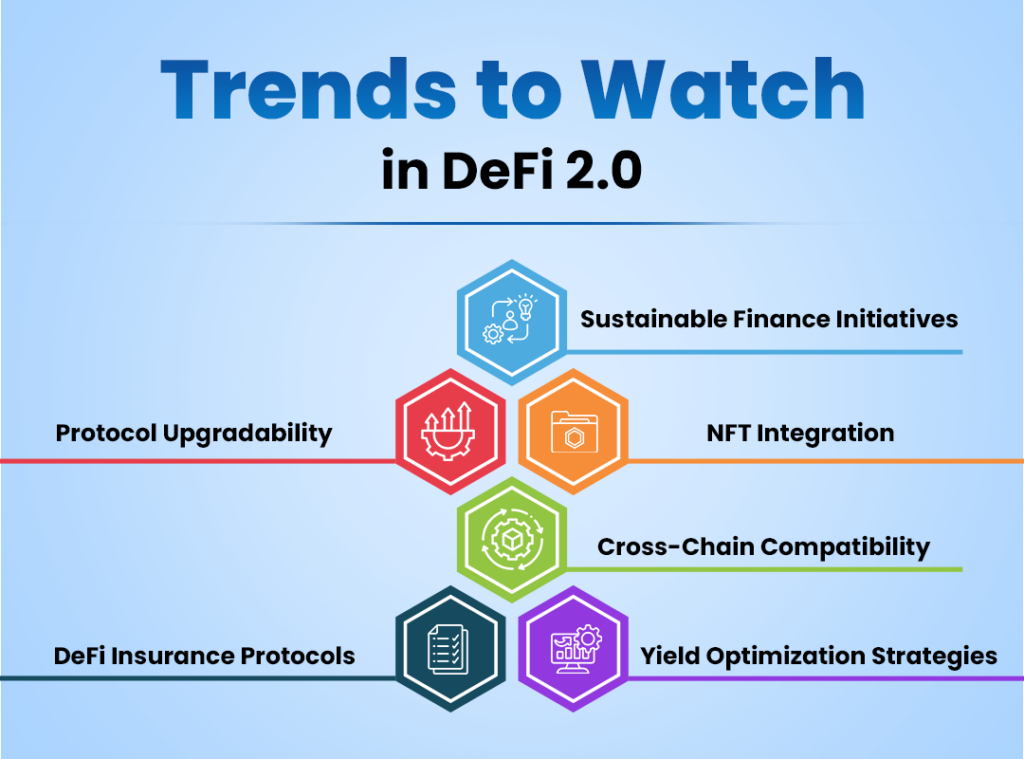
Sustainable Finance Initiatives
DeFi 2.0 is increasingly focusing on sustainability, with projects aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and promote eco-friendly practices. This includes integrating renewable energy sources and developing protocols that prioritize green investments.
Protocol Upgradability
Flexibility is key in DeFi 2.0, where protocols are designed with upgradability in mind. This allows for improvements and adaptations to new technologies or regulatory changes without requiring complete overhauls, enhancing long-term viability.
NFT Integration
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are being utilized in various DeFi applications, from collateralizing loans to representing ownership in liquidity pools. This integration opens up new use cases and enhances user engagement by merging the worlds of DeFi and digital art/collectibles.
Cross-Chain Compatibility
As the DeFi ecosystem expands, cross-chain compatibility is essential for seamless asset transfers and interactions across different blockchain networks. Protocols that facilitate interoperability are gaining traction, enabling users to leverage diverse platforms without friction.
DeFi Insurance Protocols
The emergence of insurance protocols specifically tailored for DeFi addresses risks associated with smart contract failures and hacks. These solutions provide users with peace of mind, fostering greater participation in the DeFi ecosystem.
Yield Optimization Strategies
Advanced yield optimization strategies are becoming more common, utilizing algorithms and AI to automatically allocate assets for maximum returns. These strategies help users navigate the complex landscape of yield farming and liquidity provision.
Future of DeFi 2.0
The future of DeFi 2.0 is inclusive and efficient as well. DeFi 2.0 is said to bring financial services to a global audience, moving from traditional banking systems. Innovations such as self-repaying loans, advanced yield farming strategies, and protocol-controlled liquidity can help improve stability and attract participants. But regulatory challenges, as well as smart contract risks, remain and need careful navigation. DeFi 2.0 is expected to continue its ascent in upcoming years, which would offer individuals greater financial freedom and access to a wide array of decentralized services.
Conclusion
DeFi 2.0 marks a transformative phase in the evolution of decentralized finance. It has emerged as a dynamic and innovative ecosystem that seeks to address the limitations of its predecessor. The emphasis of DeFi 2.0 on decentralization, security, and scalability signifies a maturation of the DeFi space. DeFi has some of the best features, such as impermanent loss insurance, advanced yield farming strategies, and self-repaying loans. Such innovations help mitigate user risk and encourage broader participation and investment in the DeFi ecosystem.





What do you think?
It is nice to know your opinion. Leave a comment.